Nestled between vast desert expanses and the Red Sea, Saudi Arabia stands as a testament to timeless traditions, juxtaposed against modern grandeur. This land, rich in historical sites and cultural tapestries, is a bridge between ancient civilizations and futuristic urban landscapes. From the hallowed grounds of Mecca to the glittering skyline of Riyadh, Saudi Arabia beckons with its blend of spiritual pilgrimage and cosmopolitan allure.
When visiting, always dress conservatively, honoring the nation’s deep-rooted customs and ensuring a seamless experience.
Consider hiring a local guide; they offer invaluable insights, especially when exploring historical treasures like Al-Ula or Diriyah.
Saudi Arabia: A Jewel of the Middle East
| Capital | Riyadh |
| Time in Saudi Arabia | GMT+3 |
| Language spoken | Arabic |
| Population | 34.81 million people (World Bank, 2020) |
| Religion | Islam (85%) Christianity (10%) Other (5%) |
| Currency | Saudi Riyal (SAR) |
| Airports | King Khalid International Airport King Abdulaziz International Airport King Fahd International Airport Prince Mohammad bin Abdulaziz International Airport Abha Regional Airport King Abdulaziz Air Base Airport |
Saudi Arabia: A Jewel of the Middle East, renowned for its majestic landscapes and rich heritage. Located in the Arabian Peninsula, this fascinating country boasts a history that spans thousands of years. It is home to stunning natural wonders, ancient cities, and vibrant cultural traditions.
Where is Saudi Arabia located?
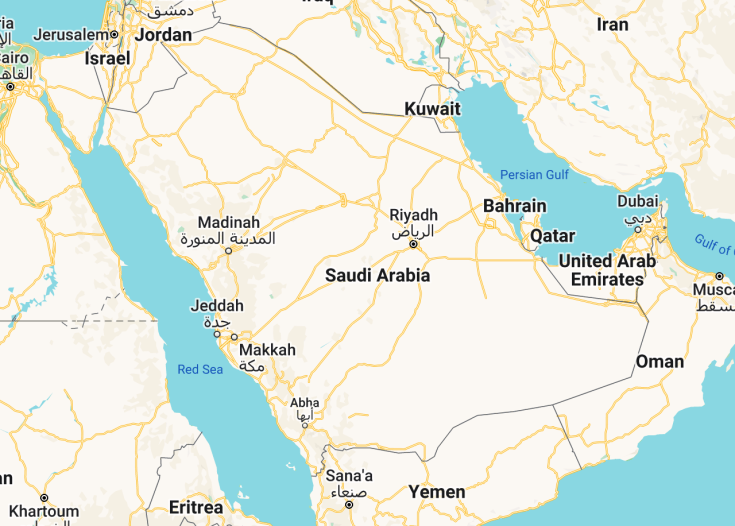
Saudi Arabia is located in the Middle East, sharing its borders with Jordan, Iraq, Kuwait, Qatar, Bahrain, the United Arab Emirates, Oman, and Yemen. It occupies a significant portion of the Arabian Peninsula, extending from the Red Sea in the west to the Arabian Gulf in the east.
What is Saudi Arabia famous for?
Saudi Arabia is famous for its historical sites, such as the ancient Nabatean city of Al-Hijr (Madain Salih), a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It is also renowned for its vast deserts, including the magnificent Rub’ al Khali (Empty Quarter), which is the largest continuous sand desert in the world. Additionally, Saudi Arabia is known for being the birthplace of Islam and home to the two holy cities of Mecca and Medina.
History
Pre-Islamic Period (up to 7th Century CE)
Long before the rise of Islam, the Arabian Peninsula was home to various ancient civilizations. Traders, settlers, and nomads have occupied its vast deserts and coastal areas, leaving behind a tapestry of archaeological wonders. The Nabateans built the rock city of Al-Ula, which became an essential caravan stop for the incense route. In the south, the Kingdom of Sheba flourished, with tales of its wealth even mentioned in biblical accounts.
Prophet Muhammad and the Rise of Islam (7th Century CE)
During the early 7th century, the Prophet Muhammad received revelations from God, leading to the foundation of Islam in Mecca. As his following grew, so did opposition from Meccan leaders, culminating in the Hijrah to Medina. By 630 CE, Muhammad and his followers returned to Mecca, establishing it as the spiritual center of Islam. The Kaaba, initially a pre-Islamic pilgrimage site, was rededicated to the monotheistic God of Islam.
Islamic Caliphates and Empires (7th-10th Century CE)
Following the death of Prophet Muhammad, the Rashidun Caliphs expanded Islamic territories, making Saudi Arabia the heartland of the burgeoning Muslim empire. Over the centuries, it fell under the rule of various Islamic dynasties, including the Umayyads, Abbasids, and Fatimids, each contributing to its rich cultural and architectural heritage.
Decline and Fragmentation (10th-18th Century CE)
Post the golden age of Islamic empires, the region saw a period of decline and fragmentation. Multiple smaller states and tribes controlled various parts of the Arabian Peninsula. Nevertheless, trade routes and the annual Hajj pilgrimage to Mecca ensured the region’s sustained significance in the broader Islamic world.
Rise of the House of Saud (18th-20th Century CE)
In the mid-18th century, Muhammad ibn Saud allied with the religious leader Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab, founding the First Saudi State. Over the next two centuries, the House of Saud would experience rise and fall, culminating in the establishment of the modern Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in 1932 under King Abdulaziz Ibn Saud. This period was marked by unification campaigns and the consolidation of political power.
Modern Saudi Arabia (20th Century CE-Present)
The discovery of oil in the 1930s transformed Saudi Arabia from a desert kingdom to one of the world’s most influential economic powers. With the influx of oil revenue, rapid modernization and infrastructural development began. The country has played a pivotal role in global energy markets and geopolitics. Today, under Vision 2030 led by Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, Saudi Arabia seeks to diversify its economy and expand its cultural influence, making significant strides in sectors like tourism, entertainment, and technology.
Visit Saudi Arabia
What to see and do in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia offers a diverse range of attractions for visitors to explore and experience. Here are some of the top things to see and do in the country:
- Visit the historical city of Mecca and Medina, the holiest sites in Islam and important pilgrimage destinations for Muslims.
- Explore the ancient ruins of Madain Saleh, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and an important Nabatean archaeological site.
- Experience the stunning natural beauty of the Empty Quarter, the largest continuous sand desert in the world.
- Discover the vibrant city of Riyadh, the capital of Saudi Arabia, with its modern architecture, shopping malls, and cultural attractions.
- Relax on the pristine beaches of the Red Sea coast and indulge in water sports such as snorkeling and diving.
- Explore the traditional markets and souks in cities like Jeddah and Riyadh, where you can buy traditional handicrafts, spices, and textiles.
- Discover the rich history and culture of Saudi Arabia by visiting the National Museum in Riyadh and other historical sites.
- Experience traditional Saudi Arabian cuisine and enjoy the hospitality of the local people.
Events in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia hosts various events throughout the year, showcasing its rich culture and traditions. Some notable events include:
- Janadriyah Cultural Festival: Celebrated in Riyadh, this festival showcases the diverse cultural heritage of Saudi Arabia through traditional music, dance, crafts, and cuisine.
- Saudi National Day: Celebrated on September 23rd, this day commemorates the establishment of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and is marked by various festivities, including fireworks and parades.
- Muslim Festivals: Saudi Arabia observes Islamic festivals such as Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha, which are celebrated with great enthusiasm and include prayers, feasts, and community gatherings.
- Camel Races: Camel racing is a popular sport in Saudi Arabia, especially during the winter season. Visitors can witness these traditional races and experience the excitement of this age-old tradition.
Best time to visit Saudi Arabia
The best time to visit Saudi Arabia is during the winter months from November to March when the weather is mild, and outdoor activities can be enjoyed comfortably. However, it’s important to note that Saudi Arabia experiences different climatic zones, with the desert regions being extremely hot during the summer months. It is advisable to plan outdoor activities and sightseeing during the cooler months to avoid extreme heat.
Is Saudi Arabia worth visiting?
Saudi Arabia is definitely worth visiting for those interested in exploring a country rich in history, culture, and natural beauty. The country offers a unique blend of ancient traditions and modern developments, providing visitors with a glimpse into its vibrant past and promising future. From the magnificent mosques of Mecca and Medina to the stunning landscapes of the Empty Quarter, Saudi Arabia has a lot to offer. However, it’s important to respect the local customs and traditions, especially in regards to dress code and behavior. Additionally, it’s advisable to check the latest travel advisories and guidelines before planning a trip to Saudi Arabia.
Common questions
What are the popular tourist attractions in Saudi Arabia?
- Al-Masjid an-Nabawi: Also known as the Prophet’s Mosque, it is one of the holiest sites in Islam and attracts millions of worshippers every year.
- Madinah Old Bazaar: Visit this vibrant market to experience the local culture, shop for traditional goods, and taste delicious street food.
- Al-Diriyah: Discover the historical district of Al-Diriyah, home to the first Saudi state and explore its fascinating architecture and museums.
- AlUla: Marvel at the ancient tombs and breathtaking rock formations in AlUla, known for the UNESCO World Heritage site, Madain Saleh.
- Masmak Fortress: An iconic landmark in Riyadh, the Masmak Fortress showcases the history of Saudi Arabia and its connection to the founding of the nation.
- Edge of the World: Enjoy panoramic views of the vast desert landscape and stunning cliffs at the Edge of the World near Riyadh.
- King Abdulaziz Center for World Culture: Immerse yourself in art, science, and culture at this renowned cultural center in Dhahran.
- Jeddah Corniche: Take a leisurely stroll along the Jeddah Corniche and enjoy the beautiful views of the Red Sea.
- King Fahd Fountain: Witness the impressive King Fahd Fountain in Jeddah, one of the tallest fountains in the world.
- Riyadh National Museum: Learn about the rich history and heritage of Saudi Arabia through fascinating exhibits and artifacts at the Riyadh National Museum.
- Dammam Corniche: Relax at the Dammam Corniche, a picturesque waterfront promenade with parks, restaurants, and recreational facilities.
- Taif: Explore the cool and mountainous city of Taif, known for its beautiful scenery, gardens, and aromatic rose farms.
What is the cuisine of Saudi Arabia?
- Mandi: A fragrant rice dish usually accompanied by tender, spiced meat such as lamb or chicken.
- Kabsa: Rice mixed with aromatic spices and served with meat, vegetables, and nuts. Kabsa variations include chicken, lamb, or camel meat.
- Shawarma: Thinly sliced marinated meat, usually chicken or beef, wrapped in flatbread with various condiments.
- Mutabbaq: A savory pastry filled with a mixture of ground meat, onions, and spices.
- Samboosa: Similar to Indian samosas, these deep-fried pastries are typically stuffed with spiced meat or vegetables.
- Harees: A hearty dish made from ground wheat and meat, often enjoyed during Ramadan.
- Jareesh: A traditional dish made from crushed wheat, cooked with either chicken or lamb, and flavored with a variety of spices.
- Masoub: A sweet dish made from mashed bananas, bread, and honey, often topped with nuts and served as a dessert.
- Arabic coffee: A traditional drink made with lightly roasted coffee beans and flavored with cardamom and saffron.
- Mamool: Small, delicately shaped pastries filled with dates, nuts, or figs.
- Muhallabia: A creamy rice or semolina pudding spiced with rose water, topped with ground pistachios or cinnamon.
- Shakshuka: A popular breakfast dish consisting of poached eggs in a rich tomato sauce with peppers and onions.
What are the traditional clothing styles in Saudi Arabia?
- Thobe: The traditional garment for Saudi men is called a thobe. It is a long, loose-fitting robe typically made of white cotton.
- Ghutra: The ghutra is a traditional headdress worn by Saudi men. It is a square-shaped scarf made from cotton or silk and is worn on the head, secured with an agal, a black cord.
- Abaya: The abaya is a loose-fitting, black cloak worn by women, covering their entire body except for their hands and feet. It is often accompanied by a niqab or hijab.
- Niqab: The niqab is a face-covering worn by some women in Saudi Arabia. It is a veil that is worn over the face, leaving only the eyes visible.
- Hijab: The hijab is a headscarf worn by women to cover their hair and neck while leaving the face exposed.
- Sheila: The sheila is a lightweight scarf worn by women to cover their hair. It is often brightly colored and can be draped over the shoulders or wrapped around the head.
- Thawb: The thawb is a traditional dress worn by Saudi women. It is a loose-fitting, ankle-length garment made of lightweight fabric.
- Bedouin clothing: In rural areas, Bedouin men and women can be seen wearing more traditional clothing, such as the bisht, a flowing cloak worn by men.
What is the climate like in Saudi Arabia?
- Hot summers: Summers in Saudi Arabia are extremely hot, with temperatures often exceeding 40°C (104°F). Some regions, such as Riyadh, can experience temperatures as high as 50°C (122°F).
- Mild winters: Winters are generally mild, with temperatures ranging from 10°C to 25°C (50°F to 77°F). Coastal areas, like Jeddah, have slightly cooler winters compared to inland regions.
- Dry climate: Saudi Arabia is known for its arid climate, with very low annual rainfall. Some areas, particularly in the northern part of the country, may experience little to no rain for several years.
- Dust storms: Dust storms, known as haboob, can occur throughout the year, especially during the summer months. These storms are caused by strong winds blowing loose sand and dust across the desert landscape.
- Seasonal variations: There are slight variations in climate across different regions of Saudi Arabia. Coastal areas enjoy cooler sea breezes, while regions closer to the desert experience hotter and drier conditions.
What are the customs and etiquette in Saudi Arabia?
- Dress modestly: Both men and women should dress conservatively and avoid clothing that is too revealing. Women should cover their shoulders and wear long skirts or pants. Men should avoid wearing shorts.
- Respect for Islamic traditions: Saudi Arabia is an Islamic country, and visitors should respect local customs and traditions. This includes being respectful towards mosques, refraining from public displays of affection, and avoiding alcohol consumption in public.
- Greeting customs: When greeting someone of the opposite sex, it is customary to avoid physical contact and instead nod or verbally exchange greetings. It is also customary to use your right hand for greetings and other interactions.
- Public behavior: Public displays of affection should be avoided, and it is important to maintain a respectful and conservative demeanor in public places.
- Conservative behavior: Avoid engaging in behaviors that may be deemed disrespectful or offensive. This includes taking photographs of local people without their consent and engaging in conversations or behaviors that are considered inappropriate.
- Gender segregation: Some public spaces, such as restaurants and public transportation, may have separate areas for men and women. It is important to follow these rules and respect the gender segregation practices.
- Food etiquette: When dining with Saudis, it is customary to eat with your right hand, as the left hand is considered unclean. It is also polite to accept offers of hospitality, including food and beverages.
- Ramadan customs: During the holy month of Ramadan, Muslims fast from dawn until sunset. Visitors should be respectful by avoiding eating, drinking, or smoking in public during fasting hours.