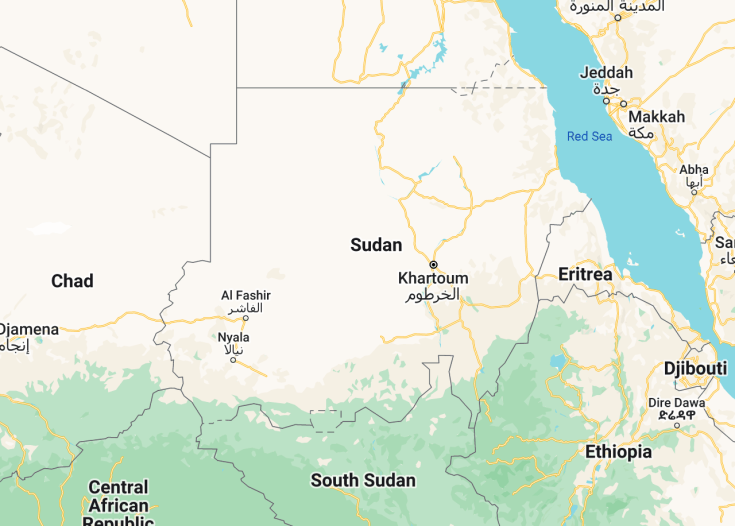
A confluence of ancient civilizations, Sudan stands as a testament to Africa’s rich history. Home to more pyramids than Egypt, its archeological wonders blend seamlessly with its vast deserts and the life-giving Nile River. Travelers seeking a blend of history and natural beauty will find Sudan an uncharted treasure trove.
When exploring historical sites, opt for knowledgeable local guides who can provide deeper insights into Sudan’s heritage.
Visiting during the cooler months, between November and February, will ensure a more comfortable exploration of Sudan’s attractions.
Sudan: land of the pharaohs and meroitic kingdoms
| Capital | Khartoum |
| Time in Sudan | GMT +2 |
| Language spoken | Arabic (official), English, and multiple indigenous languages |
| Population | Approximately 44 million (Source: World Bank, 2022) |
| Religion | Islam (97%) Christianity (1.5%) Indigenous beliefs (1.5%) |
| Currency | Sudanese pound (SDG, SDG) |
| Airports | Khartoum International Airport Port Sudan New International Airport Nyala Airport |
Encompassing vast deserts, the mighty Nile River, and a history that spans millennia, Sudan offers an alluring blend of ancient wonders and natural splendors. Once the heart of ancient Nubian civilizations, this northeastern African nation boasts a treasure trove of archaeological marvels that stand testament to its illustrious past.
The Pyramids of Meroë, lesser-known than their Egyptian counterparts but equally mesmerizing, rise majestically against the backdrop of the Bayuda Desert. These pyramids, remnants of the Kingdom of Kush, reveal the grandeur of a bygone era. Alongside, the ruins of temples, palaces, and statues narrate tales of power, faith, and artistic prowess.
Beyond its ancient relics, Sudan’s topography is a diverse mosaic, from the arid Nubian Desert to the lush banks of the Nile River. These fertile Nile banks have witnessed countless civilizations flourish and wither, each leaving behind indelible imprints. Moreover, the rich traditions and hospitality of Sudanese people, influenced by Arab and African cultures, create an inviting milieu for visitors.
While Sudan offers a myriad of attractions, it’s essential for travelers to be mindful of regional advisories and local customs. With a spirit of exploration and respect, tourists can unravel the myriad layers of Sudan’s historical and cultural fabric.
Where is Sudan located?
Sudan is situated in northeastern Africa, bordered by Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the northeast, Eritrea and Ethiopia to the east, South Sudan to the south, the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, and Libya to the northwest.
What is Sudan famous for?
Sudan is renowned for its ancient archaeological sites, particularly the Pyramids of Meroë, remnants of the Kingdom of Kush. Additionally, its rich confluence of Arab and African cultures, the expansive Nubian Desert, and the fertile banks of the Nile River contribute to its fame.
History
Prehistoric Times – Ancient Civilizations
The area known today as Sudan boasts a rich tapestry of human history, with evidence of ancient civilizations stretching back millennia. The Kingdoms of Kerma, Kush, and Meroe thrived between 2500 BC and 300 AD, leaving behind monumental relics, particularly in the areas around the Nile. These kingdoms had notable interactions with ancient Egypt, alternately warring with and ruling over their northern neighbors.
7th Century – Islamic Influence
The 7th century witnessed the gradual Islamic influence in Sudan, primarily brought by Arab traders and missionaries. Over the centuries, Islam deeply ingrained itself in the region’s fabric, influencing its culture, language, and politics. By the end of the 11th century, Christianity, once prominent in Sudan, was largely supplanted by Islam.
1821-1885 – Egyptian-Ottoman Rule
In 1821, Sudan was invaded and subsequently annexed by the Ottoman-Egyptian rulers. This period was marked by increased trade, urbanization, and infrastructural development. However, it also saw the emergence of the notorious slave trade that caused significant distress and displacement among Sudanese communities.
1885-1898 – The Mahdist State
Reacting to foreign rule and the decadence of the Ottoman-Egyptian administration, a religious leader named Muhammad Ahmad declared himself the Mahdi (guided one) and led a successful revolt. This resulted in the establishment of the Mahdist State, which lasted until the British-Egyptian reconquest in 1898.
1899-1955 – Anglo-Egyptian Condominium
Following the fall of the Mahdist State, Sudan came under the joint British-Egyptian administration, known as the Anglo-Egyptian Condominium. While Egypt retained nominal sovereignty, it was Britain that largely directed Sudan’s affairs. This period witnessed significant modernization but also sowed the seeds for the North-South divide.
1956-1989 – Independence and Civil Strife
Sudan gained independence in 1956 but soon found itself grappling with political instability and a protracted civil war between the Arab-dominated north and the African south. The animosity stemmed from disparities in economic development, religion, and governance.
1989-Present – Modern Sudan
In 1989, a coup brought Omar al-Bashir to power, beginning a regime that would last for 30 years. His reign saw the continuation of the civil war and the subsequent Darfur conflict in the early 2000s, resulting in severe humanitarian crises. In 2005, the Comprehensive Peace Agreement ended the North-South Civil War, paving the way for South Sudan’s independence in 2011. In 2019, after sustained civil protests, the Sudanese military ousted al-Bashir, leading to a political transition to a civilian-military rule. As of now, Sudan is on a path of reform and international reintegration, seeking to heal the wounds of the past and build a brighter future.
Visit Sudan
What to see and do in Sudan
Sudan offers a diverse range of attractions for visitors to explore and experience. Here are some of the top things to see and do in Sudan:
- Visit the ancient pyramids of Meroë, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
- Explore the historic sites of Khartoum, including the National Museum and the Presidential Palace.
- Experience the rich cultural heritage of Sudan by attending traditional music and dance performances.
- Discover the natural beauty of Sudan’s landscapes, including the Red Sea coast and the Nubian Desert.
- Go on a Nile River cruise and experience the stunning views along the longest river in Africa.
- Interact with the friendly local population and learn about their traditions and way of life.
These are just a few of the many attractions and activities that await visitors in Sudan. Whether you are interested in history, culture, nature, or adventure, Sudan has something to offer for everyone.
Annual Events
Sudan hosts various events and festivals throughout the year, providing opportunities for locals and tourists to celebrate the country’s rich cultural heritage. Some of the notable events in Sudan include:
- The Khartoum International Book Fair, held annually in January, showcasing Sudanese literature and promoting literacy.
- The Sudan Film Festival, featuring local and international films, held in February.
- The Sudanese Cuisine Festival, celebrating the diverse flavors and culinary traditions of Sudan, held in March.
- The Sudan Fashion Week, highlighting Sudanese fashion designers and trends, held in April.
These events offer a unique opportunity to immerse yourself in Sudanese culture and connect with the local community. The vibrant atmosphere and diverse range of activities make these events a must-visit for anyone interested in experiencing the cultural scene of Sudan.
Best time to visit Sudan
The best time to visit Sudan is during the winter months from November to February. During this time, the weather is generally mild, making it ideal for exploring outdoor attractions and historical sites. The temperatures are not excessively hot, and there is less chance of rainfall compared to other times of the year.
However, it’s important to note that Sudan can experience extreme heat during the summer months, with temperatures reaching well over 40 degrees Celsius (104 degrees Fahrenheit). The summer season, from June to September, is characterized by high humidity and occasional rainfall.
It’s advisable to check the local weather forecast and plan your visit accordingly to ensure a comfortable and enjoyable experience in Sudan. Additionally, keep in mind that some attractions or activities may have specific seasonal availability, so it’s worth researching and planning ahead.
Is Sudan worth visiting?
Sudan is a country with a rich cultural heritage, diverse landscapes, and historic sites that offer a unique and authentic travel experience. However, it’s essential to be aware of the current political situation and potential safety concerns in certain areas of the country.
Despite the challenges Sudan faces, it has much to offer in terms of natural beauty, such as the stunning Red Sea coast and the ancient pyramids of Meroë. The country’s cultural scene, including traditional music, dance performances, and local festivals, provides an opportunity to immerse oneself in Sudanese traditions and customs.
If you have a keen interest in history, Sudan’s archaeological sites and museums will fascinate you with their ancient artifacts and relics. The country’s unique blend of Arab, African, and Nubian influences creates a vibrant and diverse cultural tapestry.
However, it’s important to conduct thorough research, follow travel advisories, and exercise caution when planning a trip to Sudan. Consulting with local tour operators or seeking guidance from experienced travelers can provide valuable insights and ensure a safe and rewarding visit.
Common questions
What are the must-visit places in Sudan?
- Pyramids of Meroe
- Nile River
- Sanganeb National Park
- Dinder National Park
- Gebel Barkal
- Port Sudan
- Suwakin Island
What is the best time to visit Sudan?
Are there any restrictions or guidelines for visiting Sudan?
How do I get to Sudan?
What currency is used in Sudan?
What are the main languages spoken in Sudan?
What are the popular traditional dishes in Sudan?
- Molokhia: A stew made from jute leaves and served with bread or rice.
- Ful Medames: A dish made from fava beans cooked in a flavorful sauce and served with bread.
- Kisra: A type of fermented bread made from sorghum flour.
- Tahini: A sesame paste commonly used as a dip or added to dishes for flavor.
What is the local etiquette and culture in Sudan?
What are the transportation options within Sudan?
What are the popular traditional crafts in Sudan?
- Pottery: Sudanese pottery is renowned for its intricate designs and vibrant colors.
- Woodwork: Skilled craftsmen create beautiful wooden furniture, sculptures, and household items.
- Textiles: Sudanese textiles feature colorful patterns and designs, often handwoven by local artisans.
- Leatherwork: Leather goods, such as bags, shoes, and belts, are crafted with precision and skill.
What are the safety precautions for traveling to Sudan?
What are the popular outdoor activities in Sudan?
- Diving and snorkeling in the Red Sea: Explore the stunning coral reefs and marine life.
- Wildlife safaris in national parks: Spot a diverse range of wildlife, including elephants, lions, and giraffes.
- River cruises on the Nile: Enjoy scenic boat trips along the iconic Nile River.
- Trekking and hiking: Discover the beautiful landscapes and mountains in different parts of Sudan.
Are there any unique cultural festivals or events in Sudan?
- Eid al-Fitr: Celebrated at the end of Ramadan, this festival marks the breaking of the fast and is a time of joyous celebrations.
- Sudanese Independence Day: Celebrated on January 1st, this day commemorates Sudan’s independence from British-Egyptian rule.
- Bakhor: This traditional festival involves burning aromatic wood to create a pleasant fragrance in homes and public spaces.
- Sufi Festivals: These festivals showcase traditional Sufi music, dance, and spiritual practices.