North Korea, officially the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea, is a land of enigma and deep-rooted traditions. Despite its often-contentious international reputation, the nation showcases an intriguing blend of socialist monuments, ancient Buddhist temples, and unspoiled natural landscapes. Visiting North Korea provides a window into a world markedly different from most travel destinations, offering a unique glimpse into its rich history, art, and carefully curated culture.
Engage with an official tour operator for travel, as independent visits are not permitted. Always respect guidelines provided.
Remain conscious of cultural sensitivities, especially when photographing. It’s crucial to seek permission before capturing specific sites or events.
North Korea: a mysterious and enigmatic destination
| Capital | Pyongyang |
| Time in North Korea | GMT +8:30 |
| Language spoken | Korean |
| Population | 25.5 million (Source: World Bank, 2021) |
| Religion | State Atheism (64%) Indigenous Korean religions (16%) Others (20%) |
| Currency | North Korean won (₩, KPW) |
| Airports | Pyongyang Sunan International Airport Chongjin Airport Samjiyon Airport |
North Korea, officially the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK), remains one of the world’s most enigmatic countries. Positioned on the northern half of the Korean Peninsula, it shares borders with China, Russia, and South Korea. Historically, the region was a cradle of ancient Korean civilization, flourishing for centuries before succumbing to Japanese occupation in the early 20th century. Post-World War II, the Korean War’s aftermath cleaved the peninsula into North and South, with the DPRK adopting a unique blend of socialism and Juche ideology under the leadership of the Kim dynasty. Characterized by its self-reliance and insularity, North Korea is a nation where tradition meets modernity under its own terms.
Where is North Korea located?
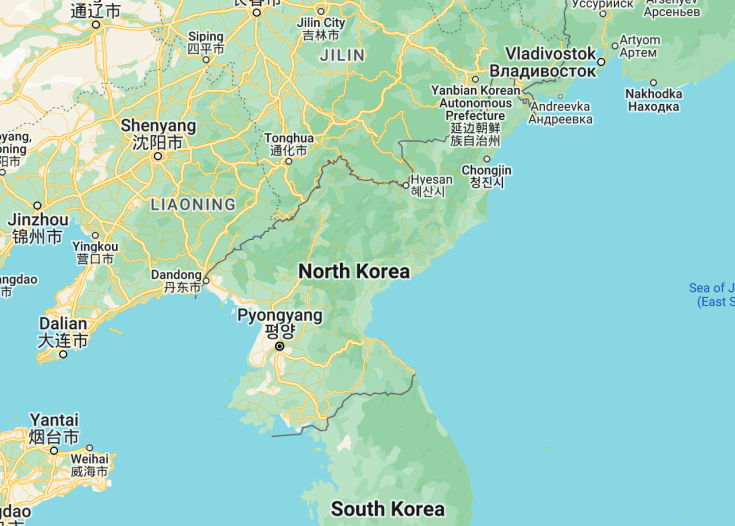
North Korea is located on the northern part of the Korean Peninsula in East Asia, bordered by China to the north, and South Korea to the south. It also shares a maritime border with Japan. This strategic location has influenced its history and geopolitical significance.
What is North Korea famous for?
North Korea is famous for its unique political system, which is based on the principle of Juche, a philosophy of self-reliance and independence. The country is also known for its military parades and displays of power, as well as its nuclear program. Additionally, North Korea is home to stunning natural landscapes, including the iconic Mount Paektu and the Demilitarized Zone (DMZ), a heavily fortified border between North and South Korea.
History
Before 1st Century BC: Ancient Kingdoms
The earliest known civilizations on the Korean Peninsula included the Gojoseon, founded in 2333 BC according to legend. It was later replaced by various warring states, including Buyeo, Okjeo, Dongye, and Samhan. These states had unique cultures, governance structures, and trade relations with neighboring regions, particularly China.
1st Century BC – 7th Century AD: Three Kingdoms Period
One of the most significant periods in Korean history was the Three Kingdoms Era, encompassing Goguryeo, Baekje, and Silla. These three states vied for dominance over the peninsula, resulting in a rich tapestry of cultural, military, and political advancements. Of these, Goguryeo, located in what is now North Korea, was the largest and most powerful.
7th – 10th Century: Unified Silla and Later Three Kingdoms
Eventually, Silla, with the help of China’s Tang Dynasty, unified the peninsula. However, this unification was temporary, leading to the Later Three Kingdoms period. During this time, the northern state of Balhae was prominent, inheriting much of Goguryeo’s cultural and territorial legacy.
10th – 14th Century: Goryeo Dynasty
The Goryeo Dynasty emerged in the 10th century, from which the name “Korea” is derived. Buddhism flourished during this period, and the world’s first metal movable type printing was developed. The dynasty had to fend off multiple invasions, notably from the Mongol Empire, leading to several shifts in its political landscape.
14th – 19th Century: Joseon Dynasty and Foreign Interventions
The Joseon Dynasty, beginning in 1392, marked a renaissance of Confucianism, literature, and science, including the creation of the Korean script, Hangul. However, the later years saw invasions from Japan and Manchu forces. By the late 19th century, Korea’s policy of isolationism came under challenge from colonial powers, leading to increased foreign influence and interventions.
Early 20th Century: Japanese Occupation
From 1910 to 1945, Korea was under Japanese colonial rule. The occupation had profound impacts on Korean society, culture, and politics. Many Koreans were forced into labor, and there was a systematic effort to suppress Korean culture and identity.
1945 – 1950: Division of Korea
Following Japan’s defeat in World War II, Korea was liberated but soon divided along the 38th parallel, with Soviet forces occupying the north and U.S. forces in the south. This division set the stage for the establishment of two separate Korean states, with the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (North Korea) being proclaimed in 1948, followed by the Republic of Korea (South Korea) in the south.
1950 – 1953: Korean War
In 1950, tensions between the two Koreas erupted into the Korean War. The conflict, involving China and UN forces led by the U.S., devastated the peninsula and solidified the division between North and South. The war ended in 1953 with an armistice agreement, but a formal peace treaty was never signed.
1953 – Present: The Kim Dynasty and Isolation
Post-war, under the leadership of Kim Il-sung, North Korea adopted a policy of self-reliance known as “Juche.” The country underwent rapid industrialization and militarization, often at the expense of civil liberties. The Kim dynasty, continued by Kim Jong-il and Kim Jong-un, has ruled with an iron fist, maintaining an isolated and highly centralized regime. Despite facing economic hardships and international sanctions, North Korea has persisted in its unique path, with a focus on nuclear capabilities and periodic diplomatic engagements.
Visit North Korea
What to see and do in North Korea
North Korea offers a unique and unparalleled travel experience for those brave enough to venture into this secretive nation. Here are some of the must-see attractions and activities in North Korea:
- Explore the capital city of Pyongyang, home to impressive monuments, museums, and landmarks such as the Juche Tower and the Mansudae Grand Monument.
- Visit the Demilitarized Zone (DMZ), the heavily fortified border between North and South Korea, and gain insight into the divided history of the Korean Peninsula.
- Experience the Mass Games, a grand performance showcasing the synchronized movements of thousands of performers.
- Discover the ancient city of Kaesong, known for its historical sites such as the Kaesong Koryo Museum and the Tomb of King Kongmin.
- Hike to the top of Mount Paektu, a sacred volcano and the highest peak in North Korea, offering breathtaking views of the surrounding landscape.
It’s important to note that travel to North Korea is heavily regulated, and tourists are only allowed to visit with an approved tour group and under strict supervision. The government controls access to certain areas and activities, and visitors are expected to follow all rules and restrictions.
Events in North Korea
Throughout the year, North Korea hosts various events and celebrations that showcase the country’s cultural heritage and political ideology:
• The Day of the Sun (April 15th) commemorates the birth anniversary of North Korea’s founder, Kim Il-sung. The capital city of Pyongyang comes alive with parades, performances, and mass gatherings.
• The Arirang Mass Games, held from July to September, is an extraordinary spectacle featuring thousands of performers, acrobatics, and synchronized displays.
• The Chosun Expo, held in October, showcases North Korea’s achievements in technology, industry, and agriculture. It provides a unique opportunity to witness the country’s advancements and innovations.
• The Pyongyang International Film Festival, held every two years in September, showcases international films alongside North Korean productions, providing insight into the country’s film industry and artistic expression.
These events offer a glimpse into North Korea’s culture, ideology, and national identity. Visitors should keep in mind that attendance at these events may be subject to government approval and restrictions.
Best time to visit North Korea
The best time to visit North Korea is during the spring and autumn seasons when the weather is mild and pleasant. From April to May and September to October, temperatures are comfortable, and the landscapes come alive with colorful blooms or fall foliage.
It’s important to note that North Korea has distinct seasons, with cold winters and hot summers. The winter months (December to February) can be extremely cold, with temperatures dropping below freezing. The summer months (June to August) can be hot and humid, with temperatures reaching over 30°C (86°F).
Visitors should also consider the timing of special events and celebrations, such as the Day of the Sun in April and the Arirang Mass Games in the summer months. Planning the trip around these events adds an extra layer of cultural immersion.
Is North Korea worth visiting?
Visiting North Korea is a decision that should be approached with careful consideration and awareness of the country’s political situation and human rights concerns. While North Korea offers unique cultural experiences and fascinating glimpses into a closed society, it is important to recognize the limitations and restrictions foreigners face while visiting.
It is crucial to note that the North Korean government tightly controls all aspects of tourism, limiting interactions with locals and restricting access to certain areas. Furthermore, the country’s human rights record has been widely criticized, and visitors must comply with strict rules and regulations established by the government.
Ultimately, the decision to visit North Korea should be based on individual beliefs, understanding the risks and limitations, and considering alternative destinations that may offer a similar cultural experience without the political restrictions. It is advisable to thoroughly research and consult with travel professionals before making a decision.